Prolotherapy
Use your own body’s power to rejuvenate and heal painful, injured joints – without surgery.What is Prolotherapy?
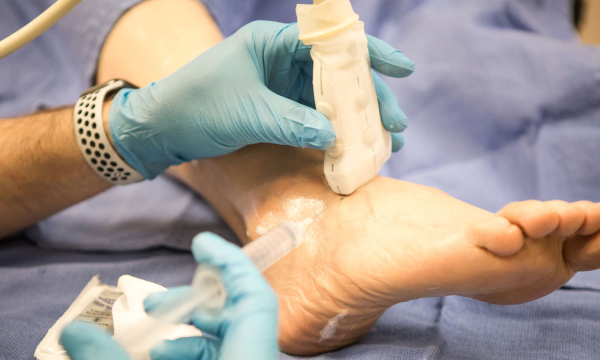
Prolotherapy is a minimally invasive, non-surgical regenerative joint injection therapy used for acute and chronic joint pain that stimulates the body’s healing process to strengthen and repair joints.
How does the injection therapy work?
We begin with a small local anesthetic, followed by an ultrasound-guided injection of a safe, natural dextrose solution directly to the painful joint, ligament, muscles, or tendon that creates lasting healing, without surgery.
What conditions can prolotherapy treat?
Most acute and chronic joint pain conditions:
- Connective Tissue Disorders
- Whiplash
- Chronic headaches
- Arthritis
- Rotator cuff injuries and tears
- Labral tears
- Meniscal tears
Prolotherapy FAQs
What is the prolotherapy solution made of?
Is prolotherapy painful?
Pain during the injection will vary based on the area being treated as well as the solution being used. We have a great deal of experience in administering these injections and do our best to mitigate as much of the discomfort as possible. We often use certain medications administered prior to the injection or Nitrous oxide (laughing gas) during the injections to improve comfort.
What should I expect after prolotherapy treatment?
It is common to have mild tissue swelling and a temporary increase in pain and stiffness. This typically passes quickly. Occasionally we will prescribe certain prescription or natural anti-inflammatory medications to help with any post-injection soreness.
How often do I need prolotherapy injections before my joints are healed?
Because cellular remodeling and repair can be slow, prolotherapy procedures are usually performed as a series. It often takes several treatments over several months to help guide the body into a gradual buildup of healthy, strong tissues that can fully support a damaged or degenerating joint.
What adverse reactions do patients have to prolotherapy?
The only adverse reaction reported is transient pain and localized swelling after injections, with overall adverse reactions being very low. The other risk factor with any interventional procedure is infection, which we minimize by using sterile aseptic techniques.
Nguyen, C., & Rannou, F. (2017). The safety of intra-articular injections for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a critical narrative review. Expert Opinion on Drug Safety, 16(8), 897–902.doi:10.1080/14740338.2017.1344211
Can I use Ibuprofen or other NSAIDs with prolothery treatment?
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like Ibuprofen are often discouraged prior to and during prolotherapy treatments. Research has shown that there can be up to 80% reduction in new cartilage growth.
NSAIDs also have been shown to accelerate the articular cartilage breakdown in osteoarthritis. Most physicians who prescribe NSAIDs for joint health do not realize that long-term use of these medications has a negative effect and dramatically increases the risk for total joint replacement.
The Acceleration of Articular Cartilage Degeneration in Osteoarthritis by Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs. Ross A. Hauser, MD. Journal of Prolotherapy. 2010;(2)1:305-322.
The effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on human articular cartilage glycosaminoglycan synthesis. J. T. DINGLE. Journal of OsteoArthritis Research Society International (1999) 7, 313–314
Articles about Prolotherapy
Keep Injuries at Bay – How to Prep for Spring Sports
Spring sports should be fun, not painful. Spring is just around the corner, which means it’s...
How Regenerative Medicine Can Help People with POTS
This post aims to empower both patients and physicians with a better understanding of POTS and the...
What is Cranial Cervical Instability, Doc?
Cranial Cervical instability (CCI) is a condition that occurs when the ligaments and...